Heart Rate Estimation from Video via CNN
Estimating Heart Rate from Video Using CNNs and Transfer Learning
Overview
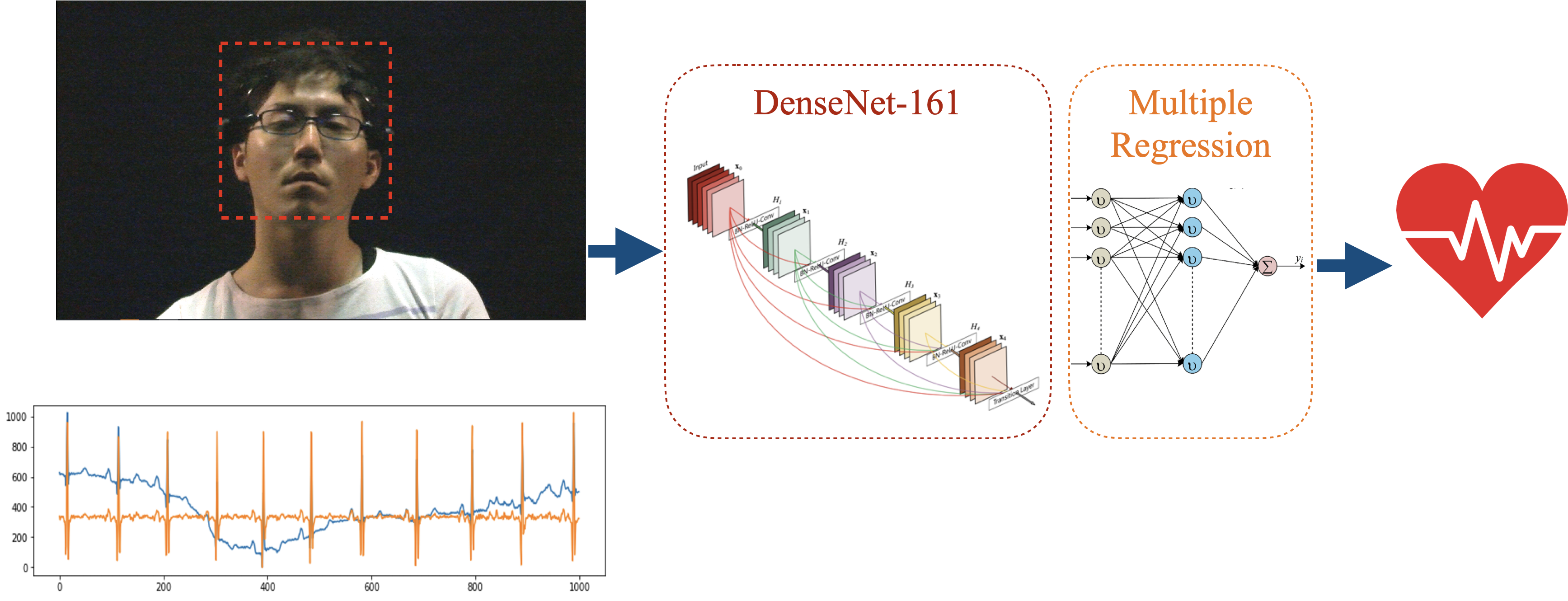
Heart Rate Estimation from Video via CNN explores a non-contact approach to estimating heart rate from facial video streams. Traditional heart rate measurements require physical sensors such as ECG or PPG, which can be intrusive and inconvenient. This project employs a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with transfer learning from the DenseNet-161 model, combined with multiple regression, to predict heart rate from facial images while participants watch video clips.
By leveraging the publicly available AMIGOS dataset, which includes ECG signals, facial videos, and emotion annotations, this project demonstrates the feasibility of remote heart rate estimation through video-based physiological measurements.
Key Features
- CNN-based Heart Rate Estimation: A CNN model with transfer learning from DenseNet-161 is used to predict heart rate from facial video frames.
-
ECG Signal Processing: ECG signals are filtered using a Notch filter to remove noise, and heart rate is calculated using a sliding window approach.
-
Face Recognition and Normalization: Faces are detected, cropped, and normalized to 128x128 pixels from each video frame, which are then used for heart rate prediction.
- AMIGOS Dataset: The project uses the publicly available AMIGOS dataset, which provides physiological signals and video data, allowing heart rate estimation to be correlated with participants’ emotions.
Study Details
-
Participants and Data Collection: The AMIGOS dataset, used for this project, consists of video recordings and physiological signals of participants watching emotional videos.
-
Training and Evaluation: Two evaluation approaches were used:
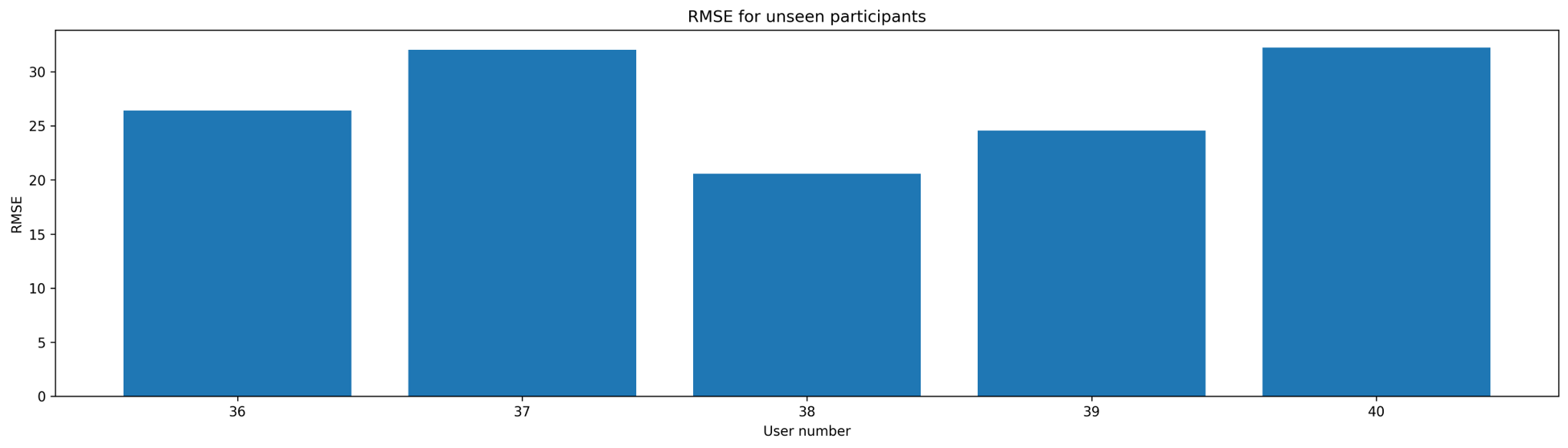
- Train on 35 participants and test on 5 unseen participants.
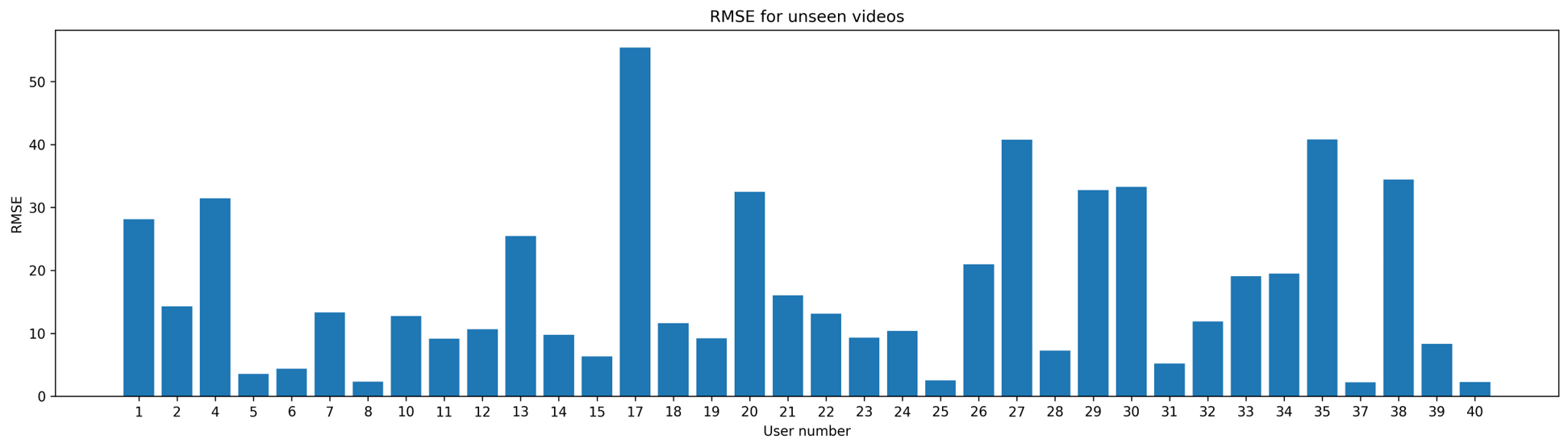
- Train on 75% of the videos from each participant and test on the remaining 25%.
The results were measured using Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE). The average RMSE for unseen participants was 27.17 bpm, and for unseen videos, it was 16.96 bpm, with a median of 12.32 bpm.
Methodology
-
ECG Signal Denoising: The project applies a Notch filter to remove noise from ECG signals, followed by a windowing approach to estimate heart rate.
-
Face Recognition and Normalization: The face-recognition package detects and normalizes faces from video frames, ensuring each face image is consistent for heart rate prediction.
-
CNN and Transfer Learning: The DenseNet-161 model is used for transfer learning, feeding facial images into a CNN. The CNN outputs are passed into a multiple regression model with three hidden layers to predict heart rate.
-
Loss Function and Optimizer: The model is trained using Mean Squared Error (MSE) as the loss function and the Adam optimizer for updating network weights.
GitHub Repository
Explore the full implementation, including the CNN model for heart rate estimation and ECG preprocessing pipeline, by visiting the GitHub repository. This repository includes code for training the model and evaluating results.
Acknowledgments
The AMIGOS dataset used in this project is publicly available and was developed for research on affect, personality traits, and mood. The dataset includes physiological signals, such as ECG and facial video recordings, which were used in this project to develop and evaluate the heart rate estimation model. For more information about the dataset, visit AMIGOS dataset.
Future Work
Possible future directions include:
- Reframing Heart Rate Estimation as Classification: Classifying heart rate into categories (e.g., normal, fast, slow) instead of predicting exact values may improve model accuracy.
- Exploring More Sophisticated Datasets: Investigating datasets with additional emotional and physiological annotations to study the correlation between emotions and heart rate.
- Improving Model Architectures: Future work could explore using RNNs or attention mechanisms to improve heart rate estimation accuracy.